Containers encapsulate applications with their dependencies, enabling portability, consistency, and scalability across diverse environments. Their lightweight nature and ability to start quickly make them a preferred choice over traditional virtual machines, empowering accelerated delivery and agile workflows.
However, containerization is not just about packaging code; it demands careful adherence to best practices to ensure security, efficiency, and maintainability. Leveraging containers properly helps organizations overcome operational complexity, reduce downtime, and fully realize the benefits of cloud native strategies.
Start with Lean and Secure Base Images
A fundamental best practice for containerization is choosing lightweight, secure base images. Using minimal images such as Alpine Linux minimizes the attack surface and reduces image size, speeding up builds and deployments. Bulky or outdated images lead to unnecessary security risks and longer startup times.
Furthermore, base images should be regularly updated and scanned for vulnerabilities using tools like Trivy or Clair. Automating this scanning process as part of build pipelines helps maintain compliance and prevent exploits in production.
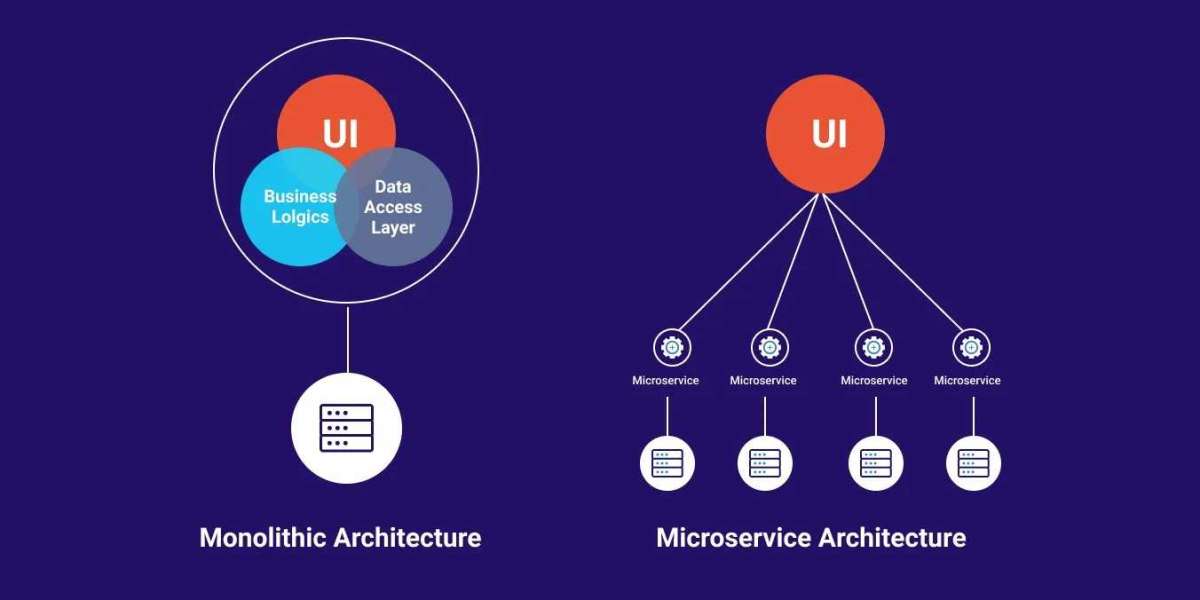
Adopt the One-Application-Per-Container Philosophy
Containers are designed to encapsulate a single application or microservice, which enhances modularity and simplifies debugging. Running multiple applications within one container negates these benefits by increasing complexity and reducing scalability.
Adhering to a one-application-per-container approach facilitates horizontal scaling, enables independent updates, and improves resource allocation. When multiple services or dependencies are required, orchestrators like Kubernetes can manage their deployment and networking, rather than bundling them tightly inside a single container.

Design for Statelessness and Immutability
Cloud native containers should be treated as stateless and immutable entities. This means data persistence should be handled outside the container via external volumes, databases, or cloud storage to ensure containers can be destroyed and recreated without data loss.
Immutability refers to building a container image once and deploying the same artifact consistently without manual changes. If updates are required, a new image is built and redeployed instead of altering running containers. This practice guarantees consistency across environments and simplifies rollback procedures.
Automate Builds, Testing, and Deployment
To fully capitalize on container agility, automating the CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment) pipelines is essential. Automating build, test, and deployment processes reduces human errors, accelerates delivery cycles, and facilitates rapid iterations.
Automation also enables continuous security by integrating vulnerability scanning, compliance checks, and image signing into the pipeline. Keeping the delivery pipeline reliable ensures faster feedback and higher confidence when pushing containerized applications to production.
Implement Robust Resource Management and Scaling
Effective containerization requires careful resource allocation within orchestration platforms like Kubernetes. Define CPU and memory requests and limits for each container to prevent resource contention and avoid node instability.
Dynamic scaling through Horizontal Pod Autoscalers adjusts the number of running container instances based on demand, ensuring optimal performance during traffic spikes and cost efficiency in quieter periods. Monitoring resource usage with tools such as Prometheus and Grafana helps detect bottlenecks and triggers scaling events proactively.
Ensure Comprehensive Monitoring and Logging
Visibility into containerized applications is critical for troubleshooting and performance tuning. Implement centralized logging and monitoring to collect container metrics, logs, and tracing data.
Solutions like ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana) or Loki for logs, combined with Prometheus for metrics, provide real-time insights into container health and behavior. Observability enables teams to quickly identify issues such as failed health checks, memory leaks, or network latency and respond before users are impacted.
Practice Least-Privilege Security and Network Segmentation
Containers share resources with the host, so security measures must be enforced at multiple levels. Run containers with non-root users wherever possible and restrict capabilities using security contexts.
Network policies should isolate container communications, allowing only necessary traffic between pods or services. Employ runtime security tools like Falco to detect anomalous behaviors and potential threats in real time.
Regular audits and adherence to zero-trust principles safeguard container ecosystems from evolving cyber risks.
Document Your Container Strategy and Maintain Consistency
Clear documentation of container build processes, configurations, environment variables, and deployment manifests is vital for team alignment and successful scaling. Version control all Dockerfiles, Kubernetes manifests, and Infrastructure as Code definitions to track changes and facilitate collaboration.

Consistent application of naming conventions, labels, and tagging facilitates management and traceability, especially in large-scale, multi-team environments.
Plan for Disaster Recovery and Backup
Even with container immutability, data persistence requires sound backup and disaster recovery strategies. Backup external data sources regularly and test recovery procedures to ensure business continuity.
Design container orchestration with fault tolerance in mind, deploying replicas across multiple availability zones or regions as needed. This approach enhances resilience and reduces downtime in case of failures.
Future-Proof Your Containerization with Expert Support
Containerization is evolving rapidly alongside emerging cloud native technologies. Staying abreast of new tools and paradigms like service meshes, serverless containers, and AI-driven monitoring adds value and keeps architectures modern.
For enterprises seeking tailored containerization strategies or end-to-end cloud native development, partnering with expert providers like those at https://symphony-solutions.com/services/cloud-native-development ensures best practices are embedded into delivery. Expert consultants bring domain knowledge, automation expertise, and security insights that accelerate container maturity and innovation.
Unlocking the Full Potential of Containerization
Adhering to these best practices in containerization empowers organizations to build highly scalable, secure, and maintainable cloud native applications. Containers offer unmatched agility and operational efficiency—but only when managed thoughtfully through automation, security, and observability.
By mastering these principles, businesses can optimize resource utilization, shorten deployment cycles, and deliver resilient digital experiences that meet modern customer demands while preparing for the future of cloud computing.