Introduction
In today's era of smart manufacturing and industrial automation , connectivity has become the foundation of operational efficiency. Two technologies — the Serial Device Server and the Industrial Gateway — play a critical role in linking traditional equipment with modern networks. They bridge the communication gap between old and new technologies, ensuring smooth data transmission, real-time monitoring, and intelligent decision-making. This article explores how these devices transform industries, enhance productivity, and future-proof operations in an increasingly digital landscape.
Understanding the Role of a Serial Device Server
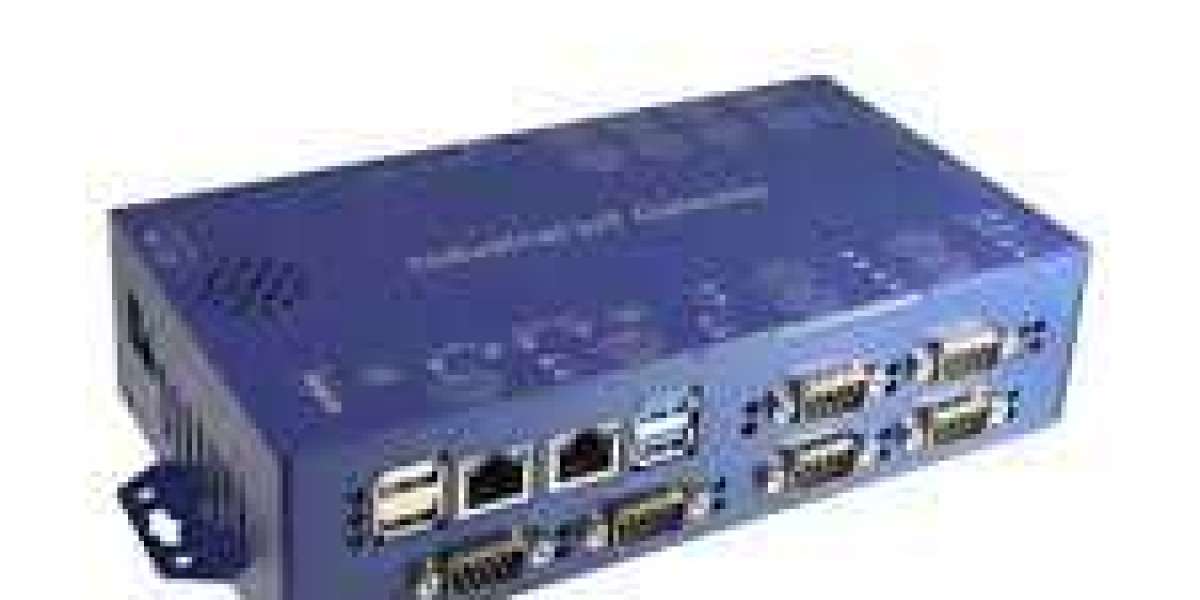
A Serial Device Server is a compact networking device designed to connect serial-based equipment, such as RS-232, RS-422, or RS-485 devices, to an Ethernet network. Many industrial machines, sensors, and controllers still rely on serial communication, a reliable but isolated protocol. The serial device server acts as a translator , converting serial data into TCP/IP packets that can travel across modern Ethernet networks.
This enables legacy equipment — like barcode scanners, PLCs, or data loggers — to communicate seamlessly with networked systems, software platforms, and cloud servers. By using a serial device server, businesses can extend the life of older hardware while integrating it into Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) environments.
Key functions of a serial device server include:
- Protocol conversion: Translates serial data to Ethernet-compatible formats.
- Remote access: Enables control of serial devices from anywhere via the internet.
- Data logging: Collects and stores data for analysis and optimization.
- Network scalability: Supports multiple devices across large industrial networks.
Through these capabilities, a serial device server bridges the past and future of industrial connectivity.
What Is an Industrial Gateway and Why It Matters
An Industrial Gateway is the next step in digital communication. While a serial device server focuses on connecting serial devices to Ethernet, an industrial gateway takes on a broader role — linking different networks, protocols, and devices across an entire operation. It serves as the central hub for data translation, security management, and communication between the factory floor and cloud platforms.
Industrial gateways are essential for IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) systems, where diverse machines use different communication protocols such as Modbus, Profibus, CAN, OPC UA, and MQTT . The gateway ensures that all these protocols work together harmoniously.
Primary functions of an industrial gateway:
- Protocol translation: Converts data between incompatible protocols.
- Edge computing: Processes data locally before sending it to the cloud, reducing latency.
- Cybersecurity management: Protects data integrity through encryption and authentication.
- Cloud integration: Transmits operational data to analytics platforms for monitoring and AI-driven insights.
In essence, the industrial gateway is the brain of the connected factory — transforming raw machine data into actionable intelligence.
How Serial Device Servers and Industrial Gateways Work Together
While both technologies serve communication needs, they complement each other perfectly in industrial automation environments. The serial device server connects older serial-based devices to Ethernet networks, while the industrial gateway integrates and manages data flow between all connected systems.
For example, in a manufacturing plant:
- The serial device server links PLCs or sensors with Ethernet systems.
- The industrial gateway collects that data, processes it at the edge, and sends key insights to a central control system or the cloud.
This collaboration enables industries to build hybrid networks where legacy systems coexist with modern IoT infrastructure — without expensive hardware replacements.
Applications of Serial Device Servers and Industrial Gateways
Both devices play vital roles across a wide range of industries:
1. Manufacturing Automation
Factories rely on serial device servers to connect older machinery to Ethernet for real-time data collection. Industrial gateways then aggregate data from multiple devices, optimize production workflows, and enable predictive maintenance.
2. Energy and Utilities
In power plants and substations, industrial gateways manage communication between control systems and remote monitoring units. Meanwhile, serial device servers ensure legacy meters and sensors remain connected and visible in modern SCADA systems.
3. Transportation and Logistics
From warehouse automation to traffic management systems, both devices ensure continuous communication between sensors, controllers, and monitoring platforms — boosting operational efficiency.
4. Oil, Gas, and Mining
Remote monitoring is crucial in hazardous or isolated environments. Here, industrial gateways provide secure remote access, while serial device servers maintain stable communication with ruggedized field equipment.
5. Building Automation
HVAC systems, lighting, and security devices often use legacy serial interfaces. By integrating serial device servers and industrial gateways , facilities can centralize control and energy management for smarter buildings.
Key Benefits of Using Serial Device Servers and Industrial Gateways
The integration of these devices brings several long-term advantages:
- Seamless Connectivity: Connects old and new technologies under a unified network.
- Cost Efficiency: Eliminates the need to replace legacy hardware.
- Scalability: Simplifies network expansion as operations grow.
- Remote Management: Enables monitoring and control from any location.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Provides real-time visibility for improved performance.
- Enhanced Security: Gateways secure critical communication channels against cyber threats.
Together, they create a robust, intelligent communication infrastructure for any industrial environment.
Choosing the Right Serial Device Server and Industrial Gateway
Selecting the right hardware depends on specific industry requirements and communication needs.
When choosing a serial device server, consider:
- Supported serial interfaces (RS-232, RS-422, RS-485).
- Number of ports and network speed.
- Compatibility with your existing devices.
- Security features like SSL encryption and access control.
When choosing an industrial gateway, evaluate:
- Supported protocols (Modbus TCP/IP, MQTT, OPC UA, etc.).
- Edge computing capabilities for data preprocessing.
- Integration options with cloud platforms.
- Redundancy, data buffering, and cybersecurity mechanisms.
Brands like Moxa , Advantech , and Siemens offer high-quality industrial-grade devices that perform reliably in demanding environments.
The Future of Industrial Connectivity
The convergence of serial device servers and industrial gateways marks a major step toward Industry 4.0 — the digital transformation of manufacturing and infrastructure. As industries continue to automate, the demand for intelligent communication bridges will only grow.
Emerging trends such as edge computing , AI-based monitoring , and 5G-enabled IoT will further enhance how these devices operate. The ability to process data closer to the source and transmit actionable insights in real-time will redefine efficiency and innovation across industrial sectors.
Conclusion
In a world where industrial systems must balance legacy hardware with next-generation technology, serial device servers and industrial gateways are the silent heroes enabling smooth, intelligent communication. They transform isolated machines into connected assets, bridge data gaps, and power the smart factories of tomorrow.
By adopting these technologies, industries gain not only improved performance and flexibility but also a foundation for sustainable digital transformation.
See more related article click here